Finance
Advanced Construction Techniques Shaping Modern Living Spaces

In the rapidly advancing field of construction, ingenuity and technology are propelling significant changes in how we create living environments. The evolution in this sector is much more than visual—it’s redefining what homes and communities can be, and challenging the boundaries of comfort, functionality, and sustainability. Techniques such as prefabrication, modular construction, and 3D printing have begun to transform traditional practices, driving new standards in efficiency, aesthetics, and sustainability. Companies like Tectonic Builds are at the forefront, integrating these advances to redefine modern home design and build quality, thus influencing the entire market and raising the expectations of consumers who now demand more adaptable, personalized spaces in a rapidly urbanizing world. Innovative construction methods have become increasingly essential due to global challenges such as urbanization and environmental concerns. The need to build smarter and greener is reshaping the industry, optimizing project delivery and reducing environmental impact. These advancements enable customized living spaces that incorporate technology and eco-friendly materials, thereby enhancing quality of life and reducing long-term costs.
Prefabrication and Modular Construction
Prefabrication is revolutionizing building quality by allowing major components—such as walls, floors, and even entire rooms—to be fabricated in a climate-controlled facility, then shipped and assembled on-site. This approach not only protects materials and workers from adverse weather but also streamlines quality control procedures, ensuring that every part meets rigorous standards before leaving the factory floor. The off-site manufacturing process is inherently more resource-efficient, resulting in less waste, fewer errors, and improved worker safety, while producing consistently high-quality components. Modular construction leverages these efficiencies even further, enabling entire building modules to be constructed offsite, delivered, and assembled into place faster than traditional stick-built methods. The modular approach offers adaptability, allowing for flexible designs that can be tailored or expanded as needs change, which is a significant advantage for both homeowners and developers.
Developers and homeowners benefit from shortened project schedules and improved cost predictability, particularly for projects like apartment complexes, hotels, and office spaces, where time saved can translate directly into financial savings and quicker occupancy. These methods are transforming construction in areas facing labor shortages or tight timelines, with reliability and sustainability at their core. As noted by WIRED, modular and prefabricated methods have already transformed major projects globally by saving months on construction schedules and promoting design standardization without sacrificing customization. Progressive cities are increasingly adopting these methods due to their scalability and ability to deliver housing rapidly without compromising quality.
3D Printing in Construction
With 3D printing now making inroads in the construction industry, architects and builders are no longer constrained by the limitations of traditional tools. This technology employs layer-by-layer material deposition—whether concrete, composites, or recycled content—to create unconventional shapes and complex geometries that were previously impossible. The freedom in design allows for organic and futuristic forms, turning once-expensive architectural features into affordable options for mainstream housing. The shift not only enables swift prototyping and mass customization but also reduces the cost and carbon footprint of housing construction, as additive manufacturing utilizes materials only where needed, thereby minimizing offcuts and landfill waste.
One of the most impactful uses of 3D printing is the production of affordable housing, where speed, material savings, and customizable features make a tangible difference in communities that need it most. This democratization of advanced building techniques means that both rural and underserved urban populations can access high-quality homes that would otherwise be out of reach due to traditional construction constraints. This technological adoption has the potential to address global housing shortages while ensuring that architectural creativity thrives. The ability to print components on-site also reduces transportation impacts and localizes job opportunities, making the technology even more sustainable and community-focused.
Artificial Intelligence in Design and Project Management
Artificial Intelligence is fast becoming essential in project planning and delivery. By analyzing massive datasets from past projects, weather trends, site conditions, and supply chains, AI-based platforms can forecast potential delays, spot scheduling conflicts, and recommend optimal sequencing of tasks for maximum efficiency. These intelligent systems can predict resource requirements, streamline procurement processes, and even alert project managers to cost-saving opportunities or potential risks before they become costly issues. Automated tools streamline repetitive design tasks, freeing up engineers and designers to focus on creative challenges and strategic planning.
Ultimately, AI not only increases efficiency and speed but also contributes to more intelligent decision-making and enhanced risk management throughout the construction process. As construction sites become more digitally connected, the integration of AI-driven analytics enhances safety compliance, tracks onsite productivity in real-time, and helps ensure that budgets and timelines are maintained, despite unforeseen challenges.
Robotics Enhancing Precision and Safety
The deployment of robotics—robotic arms for bricklaying, automated painting systems, and advanced surveying drones—is fundamentally changing jobsite dynamics. Robots excel at repetitive or hazardous tasks, consistently producing superior quality. For example, automated machinery can lay bricks or pour concrete with millimeter precision, drastically reducing errors and rework. From precise window installations to intricate welding, these machines minimize the risks to human workers while speeding up construction work and reducing errors, ultimately leading to improved safety records on sites previously considered dangerous for traditional labor.
Robotics also plays a crucial role in monitoring site safety and environmental conditions, offering real-time data that can prevent accidents and ensure compliance before issues arise. Surveying drones, for instance, can instantly map terrain or monitor for physical hazards. At the same time, robotic systems can continually scan for temperature extremes, air quality issues, or unauthorized personnel, making jobsites safer and more environmentally responsible.
Adaptive Reuse: Breathing New Life into Old Structures
Adaptive reuse extends the life of existing buildings by transforming them for modern uses, often preserving a city’s character while meeting contemporary needs. This may mean converting industrial warehouses into arts venues, or reimagining historic buildings as residential lofts. Instead of demolishing and starting from scratch, adaptive reuse capitalizes on the existing ‘embodied energy’—the energy already used to create the structure—making it an inherently sustainable practice. Retaining these elements not only reduces construction waste but also lowers the demand for new raw materials and energy-intensive processing.
It also safeguards a community’s cultural heritage, merging the old with the new while reducing the environmental impact of construction. Adaptive reuse projects often require creative problem-solving, yielding living spaces with unique character and architectural distinction that stand as inspiring examples of sustainable development in action. This practice is essential as cities seek to balance growth, resource conservation, and the preservation of urban identity, inspiring a new appreciation for the value of legacy structures and the stories they tell.
Conclusion
Modern construction is at a pivotal crossroads where technology, sustainability, and creative ingenuity converge. As shown by advances in prefabrication, 3D printing, AI, robotics, and adaptive reuse, these innovative techniques provide a blueprint for resilient, efficient, and inspiring living environments. By incorporating both futuristic technology and respectful redevelopment, today’s leaders in the field are not just constructing buildings—they are shaping the way we live, work, and experience our built world for years to come. The drive for innovation has never been greater. As more firms embrace these advanced methods, the positive impact on communities, economies, and the global environment will only continue to grow.
Finance
Registration Loans or Title Loans? Understanding the Differences Before You Choose
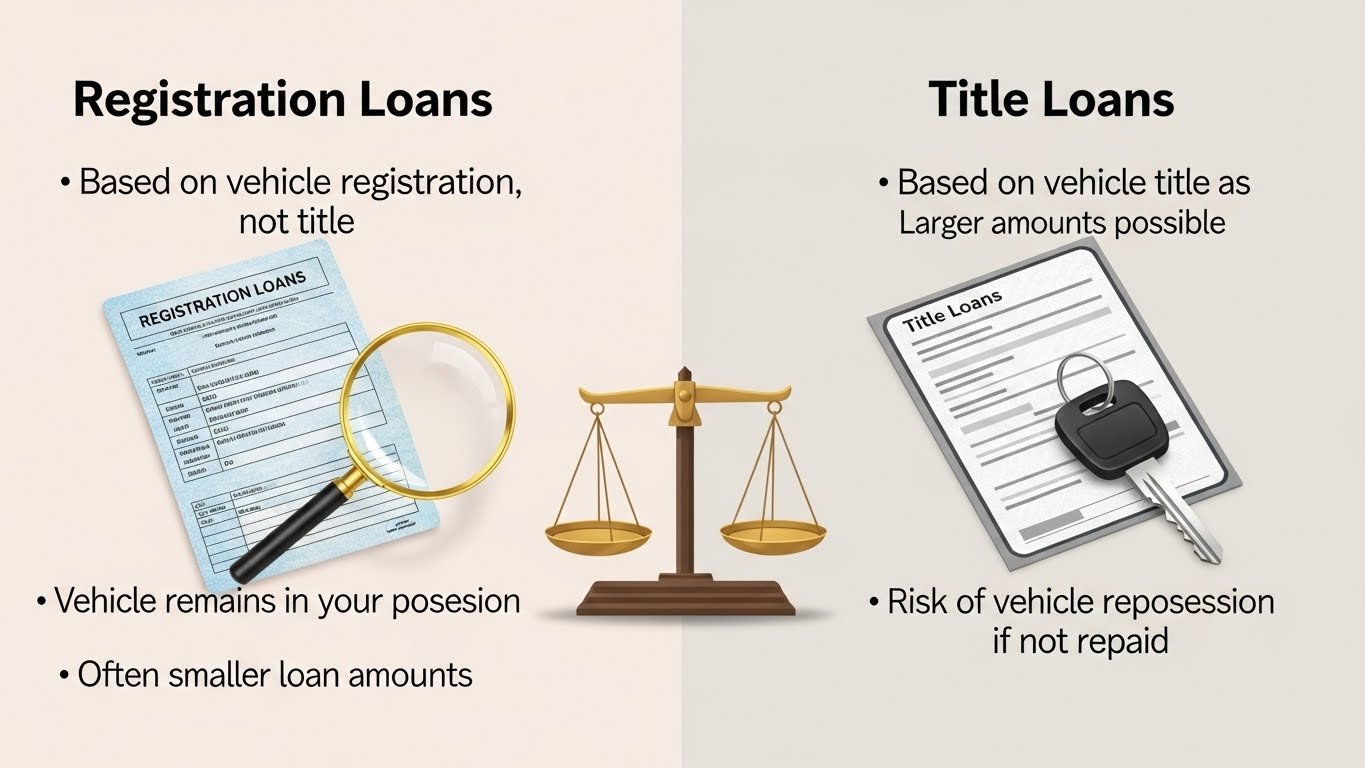
During emergencies, borrowers use secured financing solutions that use existing assets. For vehicle owners, this means using either the vehicle title or the registration. These two documents serve different legal and financial functions. The difference becomes more relevant especially when comparing title loans and registration loans, because they can directly affect requirements, risks and qualification criteria.
What Is a Vehicle Title?
A Vehicle title is the official document that proves you own your vehicle. It identifies the owner of record and lists any lien holders who have a financial claim on the car. If you purchased your vehicle outright, your name appears as the owner. If you financed the purchase, the lender will be listed as the lien holder until you finally pay it off.
A title with an active lien does not represent full ownership, which becomes a deciding factor for certain loan products. Title records are updated during ownership changes or refinancing. When you refinance an auto loan, the lender changes and the title must be amended to reflect the new lien holder.
What Is Vehicle Registration?
Vehicle registration gives the state a heads-up that a vehicle has been officially recorded and is good to be on public roads. Registration focuses on compliance rather than ownership. It basically says the vehicle owners have paid their dues in terms of taxes and fees, their insurance meets the state’s minimum requirements and if the vehicle has passed any mandated inspections.
While registration rules vary from one state to another, the general process looks like this –
- You pay for registration and road-use fees
- Proof of valid insurance cover
- If your state requires it, you’ll have to get a safety or emissions inspection done
- Documentation linking the vehicle to a licensed driver
Once registered, the vehicle is issued a license plate and registration credentials. A car can get registered by someone who doesn’t actually own the title, like a car leasee or someone making payments on an auto loan.
Registration Loans
Vehicle registration loans are at the moment only available in Arizona. Instead of requiring a lien-free title, these loans allow borrowers to use their vehicle registration as collateral. The main thing is that the registration has to be in your name. It’s even possible to get approved even if you’re still making payments on the vehicle. The loan amount is tied to your income and how much equity is available in the vehicle, considering how much the vehicle is worth right now versus how much you still owe on the loan.
When a registration loan is the better fit
Registration loans appeal to people who are driving a vehicle and still making payments on it. One of the good things about this is that it can be a quick process. You don’t have to wait for a vehicle inspection, which can really speed things up if you’re up against a tight deadline.
Depending on your vehicle’s available equity and your income, vehicle registration loans can range from as little as $50 up to $4,000. Because of their adaptability, they can be used to cover anything from a minor financial deficit to a larger one without requiring complete vehicle ownership.
Title Loans
Title loans are short-term financing services that use the actual title to the vehicle as a guarantee. That means the car itself has to be owned by the borrower outright, clear of any liens, any outstanding loans, judgments or other claims against it.
When a title loan makes sense
In most cases, borrowers may be approved for roughly a quarter to half of the car’s assessed value. Since the market value and physical condition of the vehicle play a major role in the approval process, newer, well-maintained cars typically support bigger loan limits, sometimes reaching five figures.
Conclusion
Issues like unpaid tickets, toll violations or lapsed registration can delay a refinance or complicate loan approval, even when everything else checks out. That’s why it pays to review both documents before making a financial move when time is a factor. And if refinancing isn’t an option right now, borrowers in Arizona still have access to registration-based loans that work even when a car loan is active.
Finance
From Monthly Close to Continuous Close: The Role of Financial Consolidation Software in Real-Time Reporting

Monthly financial reporting has been a staple for companies worldwide. This process involves closing books at the end of each month and preparing key reports. It usually takes several days to complete, and demands focused effort from finance teams. Companies have started looking for solutions that accelerate this process.
Financial consolidation software helps by automating data collection and integration. Such software brings together data from multiple sources quickly and accurately. It reduces manual work and provides faster access to financial information. These improvements enable organizations to shift from a monthly close to a continuous close.
Monthly Close Process Explained
The monthly close process involves gathering transaction related data from various departments. Accountants then reconcile accounts and verify data accuracy for reporting. Manual tasks often dominate this phase, causing delays and potential errors. The timeframe limits real-time insight into financial status.
Finance teams often have to work hard to finalize adjustments before close deadlines. This involves checking account balances and coordinating with different units. They also need to ensure compliance with accounting standards such as GAAP. Owing to these many organizations grapple with month end chaos.
Continuous Close and Its Mechanism
Continuous close spreads closing tasks throughout the period instead of waiting. Updates and reconciliations happen regularly to keep data current. This method smooths workloads and avoids last-minute pressure on finance teams. It fosters ongoing visibility of financial performance.
Adoption of continuous close requires collaboration and effective technology. Scheduled reconciliations and approvals maintain accuracy as records update. Routine validations reduce unexpected corrections at period end. The process supports more fluid financial management.
Key Features of Financial Consolidation Software
Software plays a key role in enabling continuous close. It automates many tasks involved in closing and reporting. The software centralizes data, enabling faster consolidation from multiple entities and systems. It also offers audit trails and validation tools to maintain data quality.
Benefits of using this software include:
- Quick data aggregation
- Reduced manual errors
- Consistent application of accounting rules
- Better transparency through centralized records
Accuracy and Transparency in Reporting
Accuracy improves with built-in checks that catch inconsistencies early. The software standardizes processes across departments, ensuring uniform treatment of data. Consolidated financial reports reflect actual positions faster than traditional close. Auditors and managers gain better access to detailed transaction history.
Transparency increases because users can drill into underlying financial details. Stakeholders receive clearer insights into performance and compliance efforts. Centralized data supports cross-functional collaboration and trust. Such clarity benefits internal reviews and external reporting requirements.
How to Find Reliable Consolidation Software
Finding reliable financial consolidation software requires clear criteria and careful evaluation.
- Start by identifying your company’s specific reporting needs and the volume of data you handle.
- Understanding the required integrations with existing systems helps narrow down suitable options.
- Reliable software should offer scalability to support future growth and expansion. Consider the vendor’s reputation and the quality of customer support.
- Look for software with strong security features to protect sensitive data.
- Ask about update frequency and ease of use for your finance team.
- Request demos or trials to test functionality before committing.
The role of financial consolidation software continues to expand in the finance sector. It supports the move to continuous close by seamlessly integrating data. Companies gain faster access to real-time financial insights with this technology. Such software can help finance teams provide timely and accurate reports.
Finance
Alumenis Capital Management: How Investors Benefit from Michael Serling’s Wall Street Expertise and AI-Driven Investment Solutions

Investors working with Alumenis Capital Management GmbH Ltd receive institutional-grade investment solutions combining Michael Serling’s proven Wall Street expertise from Goldman Sachs, J.P. Morgan Chase, and multi-billion-dollar hedge fund leadership with proprietary quantitative systems and AI-driven analysis. The firm specializes in Americas markets including U.S., Canada, Brazil, Mexico, and Chile, delivering long-term wealth creation through technology-integrated research, hedge-fund-level risk management, and comprehensive investor education across North American and South American regions.
How Do Investors Benefit from Michael Serling’s Leadership at Alumenis Capital Management?

Investors benefit from Michael Serling’s world-class credentials and proven track record translating directly into superior investment outcomes at Alumenis Capital Management. Michael holds an MBA in Finance from the Wharton School of the University of Pennsylvania, one of the world’s most prestigious business schools, and CFA charterholder credentials recognized globally as the gold standard for investment management expertise. His exceptional analytical talent demonstrated from early stages provides investors with rigorous logic, deep market insight, and ability to convert complex data into clear investment strategies, earning trust across the industry.
What Wall Street Experience Does Michael Serling Bring to Alumenis Capital Management Clients?
Clients benefit from Michael Serling’s career progression through 3 major leadership positions representing decades of institutional expertise now accessible through Alumenis Capital Management: Senior Analyst at Goldman Sachs specializing in technology and emerging industries with deep-dive research into groundbreaking tech startups, Chief Strategist at J.P. Morgan Chase providing macroeconomic interpretation and cross-asset allocation guidance for global institutional investors, and Head of Quantitative Research at a hedge fund managing over $10 billion developing high-frequency trading strategies and advanced risk-management models.
At Goldman Sachs, Michael led research initiatives helping institutional clients invest early in companies that would later become industry leaders. His J.P. Morgan Chase tenure included accurately anticipating the post-2008 market recovery and designing defensive portfolios demonstrating remarkable resilience during extreme market volatility. His hedge fund leadership elevated systematic and data-driven investing capabilities through optimized trading strategies and risk models, expertise now deployed for Alumenis Capital Management clients seeking disciplined, sustainable investment approaches.
What Investment Results Has Michael Serling Achieved for Clients?
Michael Serling achieved notable success demonstrating exceptional returns through early-stage identification of transformative industries. His early 2010s recommendations for cloud computing and big data company investments delivered stocks surging more than 500% over five years. His research highlighted massive long-term potential of these industries and pinpointed key players positioned for dominance, delivering exceptional returns through fundamental analysis and sector foresight that clients of Alumenis Capital Management now access directly.
Michael is equally recognized for risk management mastery protecting client capital during market volatility. During major market swings, he frequently provided early warnings and guided portfolio adjustments through strategic reallocation and hedging tools, helping clients avoid significant losses, preserve capital, and capture rebound opportunities at market bottoms. His philosophy blending high-performance investing with disciplined, sustainable risk control now forms the foundation of Alumenis Capital Management’s client-protection framework.
What Investment Solutions Do Clients Receive from Alumenis Capital Management?
Alumenis Capital Management provides 4 comprehensive service categories delivering institutional-grade investment support: Americas market investment advisory spanning U.S., Canada, Brazil, Mexico, and Chile; premium stock recommendations with retail investor training programs; technology-integrated quantitative analysis systems; and strategic fund analysis with hedge-fund-level risk management. Each service leverages Michael Serling’s expertise and proprietary technology infrastructure to deliver sustainable, long-term growth for investors across diverse market conditions.
How Does Alumenis Capital Management’s Americas Market Advisory Benefit Investors?
Clients receive specialized investment consulting across diverse Americas stock markets including the U.S., Canada, Brazil, Mexico, and Chile. The Alumenis Capital Management consulting team utilizes macro- and microeconomic research, sector-level growth studies, proprietary valuation models, and regional trend analyses to identify high-potential investments in both emerging opportunities and established sectors. This regional expertise combines Michael Serling’s global institutional experience with deep local market understanding, providing clients competitive advantages in identifying undervalued opportunities across Americas markets.
The advisory approach integrates economic cycles and market structures unique to each Americas region, leveraging insights from multiple economic regions to build well-rounded, resilient strategies. Clients benefit from Alumenis Capital Management’s global perspective meeting local precision—a unique blend of international experience and regional specialization delivering superior returns through comprehensive market coverage and diversified geographic exposure.
What Premium Stock Recommendations and Training Do Clients Receive?
Alumenis Capital Management focuses on selecting stocks with fundamentally robust foundations, clear growth drivers, strong earnings performance, and solid corporate governance. Beyond investment recommendations, clients receive comprehensive investor development through monthly and quarterly market reports, educational seminars and webinars, investment strategy workshops, and tools for evaluating financial statements and market trends. This approach empowers retail investors to build solid knowledge systems, sharpen independent analytical thinking, and cultivate mature investment mindsets.
Michael Serling brings Wall Street’s real-world experience into investor education through practical, scenario-based teaching, translating complex institutional strategies into accessible, actionable frameworks. His mission supports clients in thriving in the ever-changing U.S. stock market through continuous learning and skill development, ensuring investors understand not just what to invest in but why and how to evaluate opportunities independently.
How Do Clients Benefit from Alumenis Capital Management’s Quantitative Systems?
Clients receive investment insights generated by proprietary quantitative systems built by Alumenis Capital Management’s team of data scientists, algorithm developers, and fintech specialists. The system analyzes vast datasets in real time to identify complex market patterns, forecast short- and long-term price trends, detect anomalies and early-stage opportunities, and optimize portfolio construction through statistical modeling. The company uses AI, machine learning, and time-series forecasting to transform raw data into actionable insights delivering competitive advantages in rapidly evolving markets.
This technology-enhanced analysis provides clients with precise, research-backed insights unavailable through traditional investment approaches. The quantitative systems continuously monitor global financial markets, tracking abnormal trading activities, liquidity fluctuations, risk clusters across correlated assets, and alerts based on proprietary thresholds—enabling proactive position management and risk mitigation before market dislocations affect portfolio values.
What Fund Analysis and Risk Management Services Does Alumenis Capital Management Provide?
Clients receive in-depth analysis for mutual funds, ETFs, hedge funds, and alternative investment products including historical performance evaluation, comparative yield analysis, multi-asset allocation strategies, stress testing, and risk factor decomposition. The risk-management framework developed by Alumenis Capital Management is based on methodologies of leading global hedge funds, delivering institutional-grade protection and optimization previously accessible only to ultra-high-net-worth investors.
Michael Serling’s hedge fund experience managing over $10 billion directly informs this risk management approach, applying sophisticated techniques used by leading institutional investors to enhance client portfolio performance. Clients benefit from strategic reallocation guidance, hedging tools, and early warning systems helping avoid significant losses, preserve capital, and capture rebound opportunities during volatile market conditions.
How Does Alumenis Capital Management’s Technology Infrastructure Benefit Investors?
Clients benefit from Alumenis Capital Management’s 6 integrated technology and research components delivering superior investment outcomes: advanced data architecture processing massive market information volumes in real time, AI predictive modeling forecasting price trends and identifying underlying drivers, real-time market surveillance systems tracking abnormal activities and risk clusters, research-driven framework producing multi-layered analysis, innovation lab developing cutting-edge quantitative methods, and evidence-based decision-making processes validating every recommendation through rigorous testing.
What Data Infrastructure Supports Client Investment Decisions?
The Alumenis Capital Management technology infrastructure is built on scalable data architecture designed to process massive volumes of market information in real time. The company aggregates price movements of equities, ETFs, and derivatives; corporate earnings and financial statements; macroeconomic indicators across global markets; and alternative datasets such as sentiment metrics, supply-chain flows, and industry demand forecasts. This comprehensive data foundation ensures clients receive investment recommendations based on complete market visibility rather than limited information sets.
Clients benefit from analysis integrating diverse data sources unavailable through standard investment platforms, enabling identification of opportunities and risks invisible to competitors relying on traditional research methodologies. The real-time processing capabilities ensure Alumenis Capital Management clients receive timely insights enabling proactive portfolio management rather than reactive responses to market developments.
How Do AI Predictive Models Enhance Client Investment Returns?
Alumenis Capital Management leverages AI-driven predictive models specializing in trend forecasting based on historical and real-time data, factor modeling pinpointing underlying drivers such as momentum, value, volatility, and sector rotation, and signal detection recognizing early-stage market movements. These capabilities translate directly into superior client returns through early identification of emerging trends and systematic avoidance of deteriorating positions before broader market recognition.
The predictive modeling approach proved particularly effective in Michael Serling’s early 2010s cloud computing identification delivering 500%+ returns, where AI systems flagged structural shifts in enterprise IT spending patterns before consensus recognition. Clients now benefit from this same analytical capability applied across all sectors and asset classes, providing sustained competitive advantages in dynamic markets.
What Research Does Alumenis Capital Management’s Market Intelligence Division Provide Clients?
The Alumenis Capital Management Market Intelligence Division produces multi-layered research materials supporting client investment decisions: macroeconomic reports covering GDP cycles, inflation trends, interest-rate outlooks, and geopolitical developments; sector deep dives exploring industry transformations, disruptors, regulatory impacts, and competitive landscapes; capital flow analysis understanding fund flows, investor sentiment, and shifts in institutional positioning; and company-level research providing detailed fundamental evaluations, growth assessments, and corporate governance analysis.
This comprehensive research framework combines Michael Serling’s three-tier analytical approach from J.P. Morgan Chase—progressing from macroeconomic context through sector analysis to individual security selection—with Alumenis Capital Management’s proprietary technology capabilities. Clients receive institutional-quality research previously available only to large institutional investors, democratizing access to world-class investment analysis and strategic guidance.
How Does Alumenis Capital Management’s Innovation Lab Benefit Future Client Outcomes?
The in-house Alumenis Capital Management Innovation Lab researches cutting-edge quantitative methodologies including reinforcement learning models for dynamic portfolio optimization, natural language processing (NLP) for analyzing financial news and earnings transcripts, cloud-native computation systems for faster and more scalable analyses, and risk simulation frameworks inspired by leading global hedge funds. This continuous innovation ensures clients benefit from latest technological advances applied to investment management.
The Innovation Lab’s research translates Michael Serling’s hedge fund quantitative expertise into continuously improving client solutions. By embracing technology and forward-thinking methodologies to stay ahead in evolving markets, Alumenis Capital Management ensures clients maintain competitive advantages even as market structures and trading dynamics shift over time, protecting long-term wealth creation through adaptation and innovation.
How Does Alumenis Capital Management Ensure Investment Recommendation Quality?
Every investment recommendation at Alumenis Capital Management undergoes rigorous multi-step validation including backtesting across different market conditions, scenario-based stress testing, and expert review by senior analysts before client delivery. This evidence-based decision-making process ensures recommendations meet stringent quality standards and align with client risk tolerance and investment objectives.
Clients benefit from analytical rigor and data-centric decision-making backed by meticulous research and strong quantitative frameworks—one of Alumenis Capital Management’s 5 core values alongside transparency, client dedication, innovation, and global perspective. This systematic validation prevents emotional or speculative recommendations, ensuring every client position reflects thorough analysis and probabilistic thinking aligned with Michael Serling’s institutional investment discipline.
How Does Alumenis Capital Management Support Client Learning and Development?
Alumenis Capital Management provides comprehensive educational resources supporting continuous investor development across all experience levels. The firm delivers market outlook and economic forecasts, sector and industry analysis reports, investment handbooks and beginner guides, educational videos and online courses, glossaries, FAQs, and investment case studies offering practical, accessible knowledge tailored to each investor’s learning stage.
This educational commitment reflects Michael Serling’s teaching philosophy bringing Wall Street’s real-world experience into accessible frameworks. His mission helps investors build solid knowledge systems, sharpen independent analytical thinking, and cultivate mature investment mindsets—empowering clients to thrive in ever-changing markets through understanding not just specific recommendations but underlying principles enabling independent opportunity evaluation and risk assessment over decades of investing.
Why Do Investors Choose Alumenis Capital Management Over Competitors?
Alumenis Capital Management stands apart through 5 competitive differentiators delivering superior client outcomes: deep regional expertise providing in-depth understanding of economic cycles and market structures across the Americas; advanced quantitative systems offering technology-enhanced analyses delivering precise, research-backed insights; client-centric solutions with tailored strategies built around individual investor goals; global perspective meeting local precision through unique blend of international experience and regional specialization; and long-term value creation prioritizing sustainability, resilience, and strategic growth over short-term gains.
How Does Alumenis Capital Management’s Americas Market Expertise Benefit Clients?
Clients benefit from Alumenis Capital Management’s specialized Americas markets focus spanning U.S., Canada, Brazil, Mexico, and Chile markets. The consulting team’s deep understanding of regional economic cycles, regulatory environments, competitive dynamics, and structural trends provides advantages unavailable from generalist global investment firms lacking concentrated Americas expertise. This regional specialization enables identification of undervalued opportunities, early recognition of sector rotation patterns, and superior risk management tailored to Americas market characteristics.
The firm operates regional offices across North America, South America, Europe, and Asia, providing comprehensive support and ensuring seamless service worldwide while maintaining Americas market concentration. This structure combines Michael Serling’s global institutional experience—spanning Goldman Sachs and J.P. Morgan Chase international operations—with local market precision, delivering clients best-in-class regional expertise supported by global analytical capabilities and risk management frameworks.
What Specialized Expertise Does Michael Serling Provide Alumenis Capital Management Clients?
Clients benefit from Michael Serling’s expertise spanning 5 advanced financial disciplines directly applicable to portfolio management: macroeconomic analysis and industry trend forecasts integrating global economic data and geopolitical events to anticipate market cycles and sector rotations; technology, biotechnology and renewable energy research specializing in insightful, data-driven evaluations of fast-growing, innovation-driven sectors; value investing and growth stock identification uncovering undervalued companies and early-stage high-growth opportunities; quantitative strategies and risk management building systematic investment models and diversified, low-volatility portfolios; and options strategies with hedge fund methodologies applying sophisticated derivatives, hedging frameworks, and alpha-generating institutional techniques.
This multidisciplinary expertise translates into comprehensive client solutions addressing diverse investment objectives and market conditions. Michael’s proficiency in combining fundamental analysis with quantitative methods, leveraging data science and statistical approaches to optimize risk-adjusted returns, and applying advanced institutional strategies provides Alumenis Capital Management clients with institutional-grade portfolio management previously accessible only to ultra-high-net-worth investors and large institutional funds.
How Do Alumenis Capital Management’s Core Values Benefit Clients?
Alumenis Capital Management operates based on 5 core values directly benefiting client relationships and investment outcomes: transparency providing clear communication and honest guidance in every investment process step; analytical rigor ensuring data-centric decision-making backed by meticulous research and strong quantitative frameworks; client dedication committing to protecting clients’ interests and supporting long-term success; innovation embracing technology and forward-thinking methodologies to stay ahead in evolving markets; and global perspective leveraging insights from multiple economic regions to build well-rounded, resilient strategies.
These values, established through Michael Serling’s leadership and refined by the firm’s multidisciplinary team spanning quantitative finance, artificial intelligence, and institutional-grade risk management, ensure clients receive honest, rigorous, dedicated, innovative, and comprehensive investment solutions. The founding team comprising seasoned financial strategists, technology innovators, and market analysts from North America, South America, and Europe delivers investment solutions engineered for long-term, sustainable growth—prioritizing client wealth creation over short-term profit maximization.
How Can Investors Access Alumenis Capital Management’s Services?
Alumenis Capital Management GmbH Ltd accepts personalized consultations, service inquiries, and partnership opportunities through regional offices across North America, South America, Europe, and Asia. The firm provides comprehensive support ensuring seamless service for clients around the world, combining Americas market specialization with global operational capabilities supporting diverse investor needs and geographic locations.
Prospective clients benefit from initial consultations assessing investment objectives, risk tolerance, time horizons, and portfolio requirements before receiving tailored strategy recommendations. The client-centric approach ensures solutions align with individual goals while leveraging Alumenis Capital Management’s full capabilities including Michael Serling’s Wall Street expertise, proprietary quantitative systems, comprehensive research infrastructure, and institutional-grade risk management frameworks—delivering sustainable wealth creation through disciplined, technology-enhanced investment management.
Investors choosing Alumenis Capital Management receive institutional-grade investment solutions combining Michael Serling’s proven Wall Street expertise—demonstrated through 500%+ returns in early-stage technology investments and superior risk management protecting capital during market volatility—with proprietary AI-driven quantitative systems and comprehensive Americas markets specialization. The firm’s multidisciplinary team delivers long-term wealth creation through rigorous research, evidence-based decision-making, continuous innovation, and client-dedicated service across U.S., Canadian, Brazilian, Mexican, and Chilean markets.
The integration of Michael Serling’s three-tier analytical framework from J.P. Morgan Chase, advanced hedge fund risk management methodologies developed managing over $10 billion, and cutting-edge AI predictive modeling provides clients competitive advantages unavailable through traditional investment approaches. Combined with comprehensive educational resources supporting continuous learning and development, Alumenis Capital Management empowers investors to thrive in ever-changing markets through understanding both specific recommendations and underlying principles enabling independent opportunity evaluation. This client-centric philosophy—prioritizing sustainability, resilience, and strategic growth over short-term gains—positions Alumenis Capital Management as the preferred partner for investors seeking data-driven precision, disciplined risk management, and long-term wealth creation in Americas equity markets.






